Venture Debt Financing: What Is It, and How Does It Work?
by Admin
Posted on 06-07-2023 08:37 PM
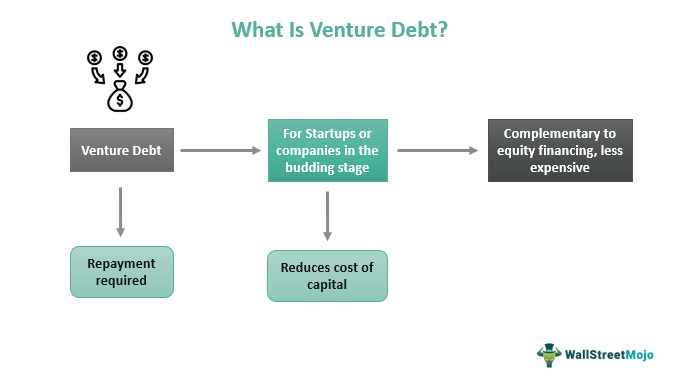
Venture debt, also known as venture lending, is a smart and critical source of financing for today’s entrepreneurial companies.
 It’s a type of financing that is offered to growth-stage venture capital-backed companies and allows a
company
to raise additional capital to supplement their equity financing and continue to fuel their growth trajectories. Venture capital is typically the first source of institutional financing for startup companies. With strong venture capital investors, a technology bank lender will typically provide a term loan and/or receivables financing. Venture debt from trinity compliments both forms of financing and provides significant value to startup companies, venture capital firms, and technology bank lenders.
It’s a type of financing that is offered to growth-stage venture capital-backed companies and allows a
company
to raise additional capital to supplement their equity financing and continue to fuel their growth trajectories. Venture capital is typically the first source of institutional financing for startup companies. With strong venture capital investors, a technology bank lender will typically provide a term loan and/or receivables financing. Venture debt from trinity compliments both forms of financing and provides significant value to startup companies, venture capital firms, and technology bank lenders.
However, it’s doing so “less aggressively than in the past,” says writer yuliya chernova. Svb’s moves are ‘contributing to a sharply decelerating venture-debt market, which means there are fewer sources of financing at the very time more startups are struggling,” the report says. In an wsj newsletter, svb’s pace of lending is not good for the startup and venture sector. “the economy and the fundraising environment are headwinds on loan origination,” said marc cadieux, a 30-year-veteran of svb who was named president of its commercial banking division in june. “fewer companies are able to clear that key underwriting bar—do you still have the support of venture investors behind you,” he said.
What is venture debt?1 venture debt financing is a loan designed to extend runway and can be a valuable financing option to supplement venture capital for growing companies. Our bankers can advise you on the many benefits of venture debt after an equity round. Preserves ownership: venture debt offers economic upside for investors, founders and employees as the least dilutive financing option. Extends your company's cash runway: venture debt funding extends runway, providing additional time for the company to reach value milestones prior to the next equity round. Fund projects leading to growth: use venture debt to hire or bolster a sales team, enhance marketing initiatives, invest in research and development or buy capital equipment.
In march, the media was inundated with analysis of the silicon valley bank (svb) collapse. One perspective that seems to be more soft-spoken than others is that of venture debt funds (vdfs), which are distinct from commercial banks (cbs), lending to technology companies. This difference between these two financing sources is important. With the recent news, the word “venture debt” seems to be conflated across cbs and vdfs, but the two can be quite distinct for borrowers or a venture equity investors or board members. For example, an asset-back revolver (such as an inventory line) from a bank might be called venture debt, but so might a senior secured term loan from a private debt fund, even though the latter is twice as expensive and far more flexible.
What is Venture Debt?
The collapse of silicon valley bank (svb) was not the end of venture debt , but it was likely the end of companies raising venture debt with the same ease that many were accustomed to.
 Techcrunch+ recently spoke to five different vcs about the state of venture debt in the wake of svb and then first republic bank’s collapse, and all of them said they don’t think the recent bank failures signaled the end of venture debt. Rather, they expect the process of raising this kind of debt will start to look a lot different. How will it change? while several investors felt venture debt will remain a cheaper option for founders than equity, all of them agreed that it would get more expensive in the future.
Techcrunch+ recently spoke to five different vcs about the state of venture debt in the wake of svb and then first republic bank’s collapse, and all of them said they don’t think the recent bank failures signaled the end of venture debt. Rather, they expect the process of raising this kind of debt will start to look a lot different. How will it change? while several investors felt venture debt will remain a cheaper option for founders than equity, all of them agreed that it would get more expensive in the future.
Written by: parker zangoei the difficult fundraising environment for venture-backed companies has made venture debt comparatively more attractive to many founders. At the same time, recent bank failures have prompted many emerging growth companies to consider private credit funds and other direct lenders as potential alternatives to their traditional bank lending partners. This alert provides context for the convergent growth of the venture debt and private credit markets and offers some key distinctions typically considered by borrowers when evaluating proposals from banks and direct lenders. Historical context lending to venture-backed companies has transformed over the past few decades from the “little brother” of the venture capital equity markets to an integral component of the broader innovation ecosystem.
Venture debt is an alternative source of capital for startups who are facing cash constraints and have difficulty obtaining financing from banks. It can help venture capitalist ("vc") backed startups in their growth journey and create an optimal funding structure, whilst enhancing stakeholders’ value. Although an established alternative financing source in the us, europe, israel and india, venture debt has recently gained traction in southeast asia as a mainstream financing option for high growth technology companies. Since its emergence in singapore in 2015, the market has seen a marked increase in venture debt activity in the region. Considered an apt support to boost the local startup ecosystem, the singapore government has introduced key programmes aimed at providing local early stage and high growth small and medium-sized enterprises an additional financing option for business growth and expansion.